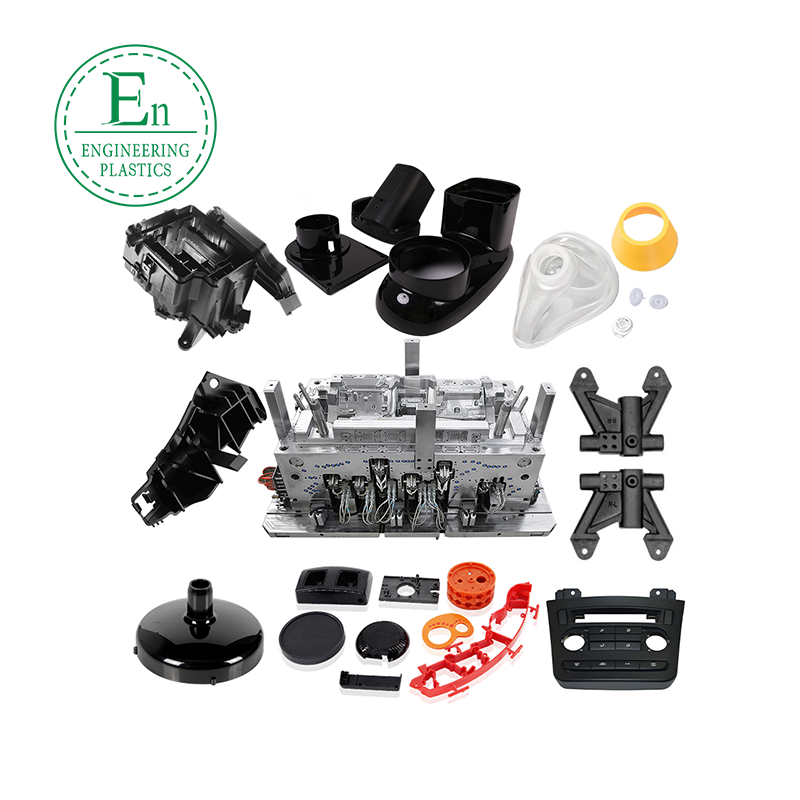
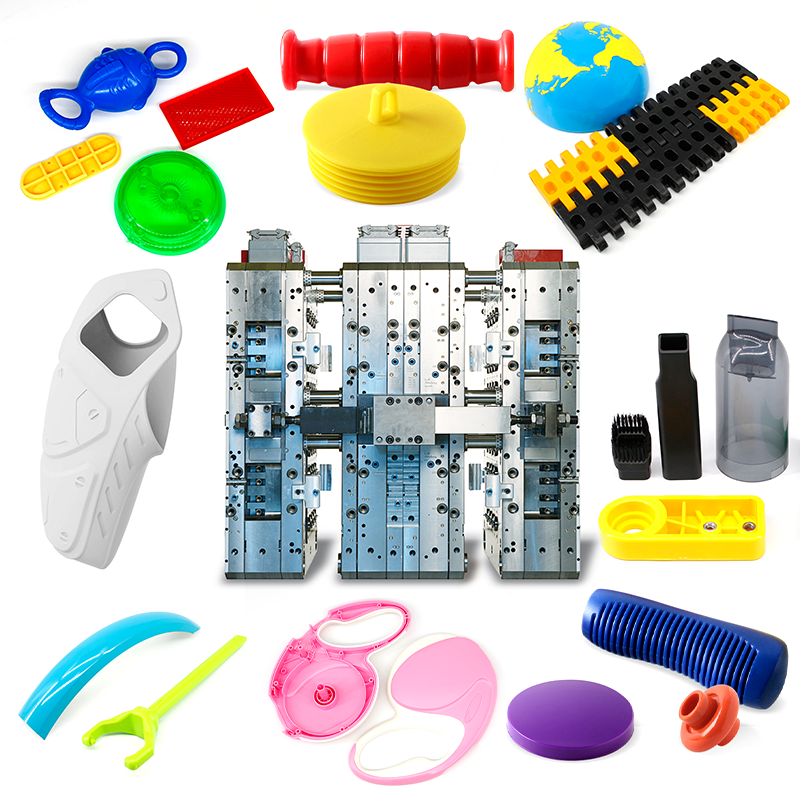
We’re Guangdong Engineering Plastics Industries Group Co., Ltd. , a specialized manufacturer of custom molds and injection molding solutions with 26 years of experience serving global clients.
Our expertise includes:
*Complex Mold Design: Multi-cavity, hot-runner, and micro-molding capabilities
*Full-Service Production: From prototyping to high-volume manufacturing
*Material Options: Engineering plastics, LSR, biodegradable polymers, etc.
*Quality Assurance: ISO 9001-certified with strict tolerance control (±0.01mm)
We’ve successfully delivered projects for industries including aerospace, automotive, robotics , and medical devices.
Our factory specializes in high-accuracy CNC machining of plastic components, utilizing state-of-the-art computer numerical control technology to deliver exceptional dimensional consistency and complex geometries. We process a wide range of engineering-grade thermoplastics including PEEK, PPS ,PAI, PI, PBI,PTFE,Nylon, ABS, POM, UHMWPE, PE,PSF, PEI, PSU, etc, catering to industries requiring tight tolerances from automotive to medical applications.
Could we schedule a call to discuss how we can optimize your next project for quality, cost, and lead time?
Email:sales@gz-plastics.com
Tel: +8618588927610
Website:https://gz-plastics.com/
In the world of modern manufacturing, few processes are as ubiquitous or essential as plastic injection molding. This technology is responsible for creating a vast array of plastic parts we use daily, from complex automotive components to simple household items. At the very heart of this powerful process lies a critical, precision-engineered tool known in French as a molde injectable. Understanding this component is the first step to appreciating the complexity and ingenuity of high-volume plastic production. This tool, often called an injection mold in English, is not just a piece of metal; it is the blueprint that gives shape to molten plastic, ensuring every single part is a perfect replica of the last.
Understanding the Core Component: The Injection Mold
So, what exactly is an injection mold, or as it's called in French, a forme d’injection? At its most basic, it is a custom-made metal block, typically constructed from high-grade steel or aluminum, that has a cavity machined into it. This cavity is the negative space of the part to be produced. The mold is usually made of two halves: the 'A' side, or cavity side, and the 'B' a side, or core a side. When these two halves are pressed together under immense pressure in an injection molding machine, they form a sealed cavity. Molten plastic is then injected into this space. The mold also incorporates several other crucial systems, including channels for cooling fluids (like water or oil) to solidify the plastic quickly, and an ejector system with pins that push the finished part out once the mold opens.
The Journey from Pellet to Part: The Molding Cycle
The process of using une forme d'injection en plastique follows a precise, repeatable cycle that allows for rapid production. It begins with the clamping stage, where the two halves of the mold are securely closed by the molding machine's hydraulic press. Next is the injection stage, where plastic pellets are melted in a barrel and the resulting liquid is injected under high pressure into the mold's cavity until it is full. The third stage is cooling. The molten plastic inside the mold cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the cavity. This is often the longest part of the cycle and is critical for the part's final dimensions and stability. Finally, the ejection stage occurs. The machine opens the mold, and an ejector mechanism pushes the solid part out, ready for collection. This entire cycle can take anywhere from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, allowing for the mass production of thousands or even millions of identical parts.
Precision Engineering: Designing and Crafting the Mold
The creation of a high-quality molde injectable is a feat of precision engineering. The design process is incredibly detailed, requiring CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to model the part and the mold itself. Engineers must account for factors like material shrinkage, the flow of plastic within the cavity, and the placement of gates (where the plastic enters) and vents (where air escapes). Once the design is finalized, the mold is manufactured using highly accurate CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and meticulous hand-polishing to achieve the desired surface finish. The quality of a molde injectable directly determines the precision, consistency, and quality of the final product. A well-made mold can last for millions of cycles, making the initial investment a crucial part of long-term manufacturing success.
The Foundation of Modern Manufacturing
In conclusion, the injection mold is far more than just a tool; it is the fundamental building block of modern mass production for plastic goods. Whether you refer to it by its English name or its French equivalents like forme d’injection or une forme d'injection en plastique, its role is undeniable. From the initial design to the final hardened steel, every aspect of the mold is engineered for precision, durability, and efficiency. This remarkable device allows industries worldwide to produce complex, high-quality parts at a scale and speed that would otherwise be impossible, solidifying its place as one of the most important innovations in manufacturing history.